Introduction to ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software system that transforms modern business management. ERP breaks down departmental barriers and fosters efficient data flow and communication by integrating and centralising various processes and functions within an organisation.
In a fragmented setup where different
departments use separate systems for their operations, ERP becomes a unifying
force. It creates a cohesive ecosystem by consolidating all critical data and
processes into a single platform, promoting data transparency and enabling
real-time data-driven decision-making. It acts as a centralised database that
stores and manages essential business information, making it accessible to
employees at all levels.
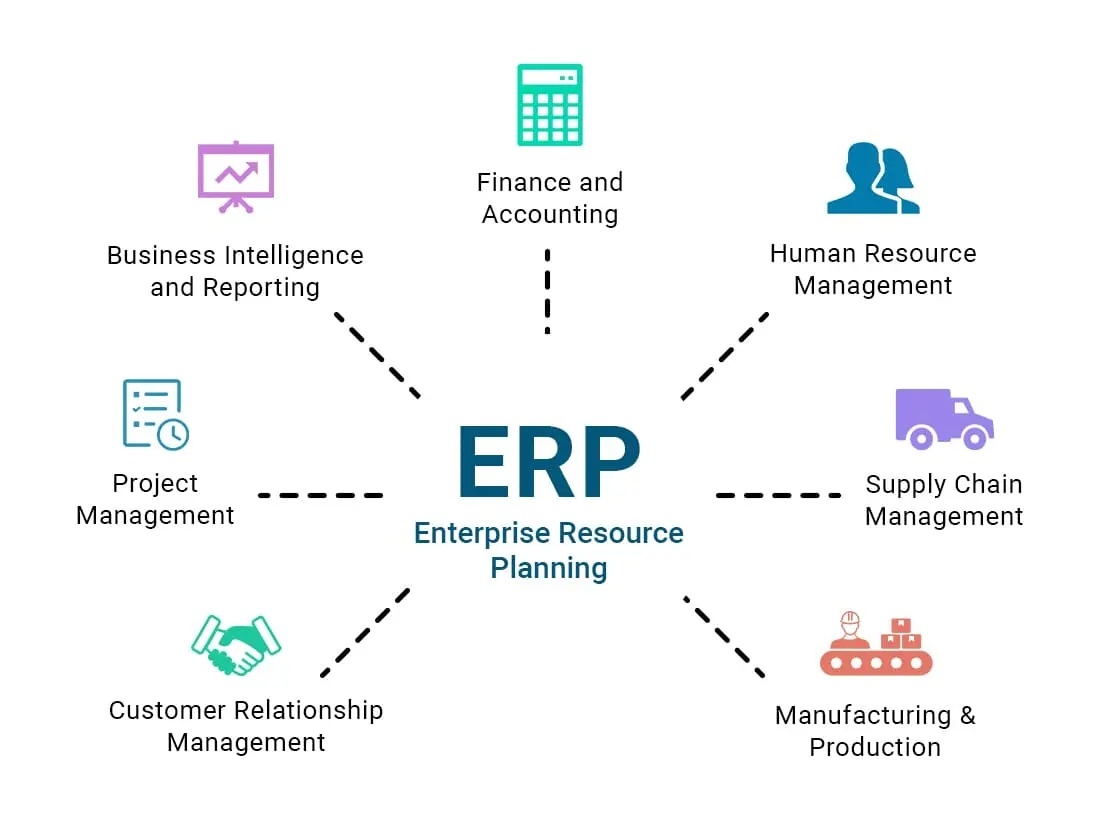
Key Components of ERP System
The key components of
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) encompass a diverse array of modules that
collectively form a comprehensive and integrated system. Each component focuses
on specific functional areas within an organisation, ensuring that essential
business processes are streamlined and optimised. Let's explore the key
components of ERP in detail:
1. Finance and
Accounting
The finance and accounting module within ERP systems serves as the cornerstone of robust financial management. It includes accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, financial reporting, budgeting, and cash management.
Accounts Payable
Streamlines outgoing payments to suppliers and vendors, ensuring prompt and accurate transactions.
Accounts Receivable
Manages incoming payments from customers, optimising invoicing and collections for a smooth cash flow cycle.
General Ledger
Acts as the central repository for all financial transactions, offering a comprehensive view of the organisation's financial health. It helps in generating accurate and real-time financial statements.
Financial Reporting
Provides customisable reports on various financial aspects, enabling data-driven decision-making. These reports include balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and profitability reports.
Budgeting
Facilitates the creation, management, and tracking of budgets across
departments and projects, aiding resource allocation and adherence monitoring.
2.
Human Resources
Management (HRM)
The HRM module in ERP is a comprehensive solution for managing various aspects of human resources within an organisation. It helps in enhancing workforce productivity, optimising talent management, and ensuring compliance with labor laws.
Recruitment and Onboarding
Streamlines the hiring process, from creating job postings to conducting interviews and handling onboarding for new employees.
Employee Records
Acts as a centralised database for employee information such as job history and performance evaluations, facilitating efficient decision-making for HR professionals and managers.
Payroll Processing
Automates salary calculations, tax deductions, and other payroll tasks, ensuring accurate and timely payments.
Benefits Administration
Manages employee benefits like insurance, retirement plans, and leave management.
Performance Management
Supports setting performance goals, conducting reviews, and providing feedback to foster employee growth.
Talent Development
Helps in identifying skill gaps, scheduling training sessions, and tracking employees' progress to enhance their skills and performance.
The HRM module in ERP
boosts employee satisfaction, and productivity, and fosters a positive organisational
culture by streamlining HR operations and ensuring compliance.
3. Supply Chain
Management (SCM)
The SCM component within ERP optimises the flow of goods and services, ensuring efficient tracking of inventory, supplier management, order fulfillment, and demand responsiveness.
Procurement
Streamlines sourcing and purchasing, securing goods and services at favorable prices from reliable suppliers.
Inventory Management
Tracks inventory levels and monitors stock movements, providing real-time visibility and reducing stockouts and carrying costs.
Order Fulfillment
Helps in processing customer orders promptly and accurately, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention.
Logistics and Distribution
Plans and manages the efficient movement of goods, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery timelines.
Supplier Relationship Management
Enables monitoring supplier performance, negotiating contracts, and maintaining a supplier database to foster strong, lasting relationships.
By providing real-time data and optimising
supply chain processes, the SCM module in ERP enables organisations to respond
swiftly to demand changes, minimise inventory costs, and ensure a seamless flow
of goods and services.
4. Manufacturing and
Production
For organisations involved in the production of goods, the manufacturing and production module within ERP plays a pivotal role in optimising manufacturing processes and resource allocation. This component streamlines production planning, scheduling, shop floor management, quality control, and product lifecycle management.
Production Planning
Enables strategic creation of production schedules to align with customer demand, which helps in effectively managing resources and minimising lead times.
Scheduling
Helps to allocate resources, machinery, and labor to specific production tasks, reducing bottlenecks and downtime.
Shop Floor Management
Empowers shop floor supervisors and managers by providing real-time visibility into work orders, resource utilisation, and production progress, enabling better decision-making.
Quality Control
Implements checks and inspections at various stages of production to ensure products meet required standards and are defect-free.
Product Lifecycle Management
This enables tracking product revisions, managing engineering changes, and optimising product development processes from design to disposal.
By optimising production processes, resource
allocation, and quality control, the manufacturing and production module in ERP
enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures consistent product quality.
5. Customer Relationship
Management (CRM)
The CRM module within ERP manages interactions with customers throughout the entire customer lifecycle. It serves as a central repository for customer data and enables fostering stronger relationships and improving customer satisfaction.
Lead Management
Helps in capturing, tracking, and nurturing leads through the sales pipeline with lead scoring, assignment, and automated follow-ups.
Sales Automation
Streamlines the sales process, allowing sales teams to manage opportunities, quotes, and sales orders efficiently.
Marketing Campaigns
Enables planning, executing, and tracking marketing campaigns for targeted and effective customer outreach.
Customer Service
Helps in providing exceptional customer support by tracking issues, assigning support tickets, and maintaining customer interaction records.
Customer Engagement and Loyalty
Helps understand customer preferences, analyse buying patterns, and deliver personalised experiences to build lasting customer loyalty.
By centralising customer data and managing
interactions, the CRM module in ERP enhances customer satisfaction, drives customer
retention, and boosts overall customer engagement.
6. Project
Management
The project management component within ERP serves as a robust tool to plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively. It provides project managers and teams with the necessary resources and features to ensure project success.
Project Planning
Helps in defining project objectives, outlines tasks, and sets timelines and milestones for well-organised project execution.
Resource Allocation
Enable project managers to assign tasks to team members based on their skills and availability, optimising resource utilisation.
Task Tracking and Management
Provides visibility into task progress, enabling project managers to identify and address bottlenecks or delays.
Budget Management
Tracks project expenses and compares them to the budget, ensuring adherence to financial constraints.
Project Reporting
Delivers detailed reports on project progress, budget adherence, and overall performance, facilitating transparent communication regarding project status.
By providing comprehensive project management
tools, the ERP system ensures that projects are completed on time, within budget,
and meet the required quality standards, contributing to overall business
success.
7. Business Intelligence
and Reporting
The business intelligence (BI) and reporting component within ERP provides valuable insights and analytics from data gathered across various modules. It offers customisable dashboards, key performance indicators (KPIs), and real-time reports, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
BI Insights
Transforms raw data into visually engaging insights, presented through customisable dashboards with critical business metrics, providing a comprehensive view of business performance.
KPI Tracking
Monitors performance against set goals, identifying areas for improvement and aligning efforts with strategic objectives.
Real-time Reporting
Offers up-to-date data and analytics for agile and data-driven decision-making.
Customised Reports
Enables users to generate tailored reports, supporting deeper analysis and exploration of business data.
By harnessing the power of BI and reporting, ERP empowers organisations to uncover trends, identify opportunities and challenges, and make data-driven decisions, driving strategic planning and overall business growth and success.
5 Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer a wide range of benefits that transform the way businesses operate and lead them to greater success. By integrating different business processes and functions into a single platform, ERP systems empower organisations with enhanced data visibility, streamlined processes, smooth communication, data security, and scalability. Let's delve into each of these benefits in detail:
1. Enhanced Data
Visibility and Real-time Insights
ERP systems serve as a single source of truth for all business data, centralising information from different departments and processes. This provides a holistic view of the organisation's performance and enables stakeholders to access accurate and up-to-date information. Real-time data visibility allows employees to make better decisions and enables agile and responsive decision-making for management.
2. Process Streamlining
and Automation
ERP system automates manual and repetitive tasks, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency. By streamlining processes such as invoicing, payroll, and inventory management, ERP saves time, minimises errors, and increases productivity. Streamlined processes lead to optimised workflows, reduced cycle times, and improved resource allocation, enhancing the organisation's competitive edge.
3. Seamless
Communication and Collaboration
ERP breaks down communication barriers, fostering a cohesive work environment. Employees from different departments can access shared data and collaborate in real time, promoting effective teamwork and problem-solving. The ERP system facilitates cross-functional communication which ensures that relevant stakeholders have access to the same information, reducing misunderstandings and improving decision-making.
4. Data Security and
Compliance
Data security is a
paramount concern for organisations. ERP systems implement robust security
measures to safeguard critical business data from unauthorised access and cyber
threats. Security features like role-based access control and encryption ensure
data is accessible only to authorised personnel. Additionally, ERP helps
organisations comply with industry regulations and data privacy laws,
mitigating legal risks and safeguarding the organisation's reputation.
5. Scalability and
Flexibility
ERP systems are
designed to scale with the growth of an organisation. ERP systems can adapt to
the changing needs of an organisation, accommodating increased data and user
requirements. Whether it's a small business expanding or a large enterprise
diversifying, ERP supports the organisation's growth. The flexibility of ERP
allows customisation to align the system with unique processes, maximising
efficiency, and effectiveness.
Incorporating ERP into Business
The process of
incorporating ERP into a business is a significant undertaking that requires
meticulous planning and thoughtful execution. ERP implementation involves a
series of steps, including analysing existing business processes, selecting the
right ERP vendor, configuring the system to align with specific business
requirements, and providing comprehensive training to employees. Moreover,
successful ERP implementation heavily depends on effective change management
strategies to ensure a smooth transition and acceptance of the new system by
all stakeholders. Let's explore each aspect of incorporating ERP into business
in detail:
1. Analysing Existing
Business Processes
Before diving into ERP implementation, businesses must conduct a thorough analysis of their existing processes and workflows. This evaluation helps identify areas that need improvement, areas of inefficiency, and opportunities for optimisation. Understanding the organisation's pain points and requirements sets the foundation for selecting the most suitable ERP solution that aligns with the company's needs and goals.
2. Selecting the Right ERP Vendor
Selecting the right ERP vendor is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of ERP implementation. Businesses should consider factors such as the vendor's track record, industry expertise, scalability of the ERP solution, and the level of support and service offered. Engaging in detailed discussions with potential vendors and conducting thorough research and reviews can help businesses make an informed choice.
3. Configuring the ERP System to Match Business Requirements
ERP systems are highly customisable, and businesses must work closely with the vendor to tailor the solution to their specific needs. Customisation allows organisations to streamline processes and workflows, and ensure that the ERP system becomes a perfect fit for the organisation's operations.
4. Providing Comprehensive Training to Employees
Employees must be well-trained to use the new system. Comprehensive training programs should be designed to cater to different roles and responsibilities within the organisation. Training should cover all aspects of the ERP system, including data entry, generating reports, and using various modules. This empowers employees to embrace the new system with confidence, leading to increased user adoption and productivity.
5. Effective Change Management
The success of ERP implementation depends on effective change management strategies. Introducing a new ERP system brings significant changes to the way employees work and interact with technology. Businesses should communicate the benefits of the ERP system and involve employees in the process from the beginning. Addressing concerns, providing support, and encouraging feedback help build trust and acceptance among employees.
Change management also involves appointing change champions within the organisation who can act as advocates for the new ERP system and support their peers during the transition. Additionally, setting realistic expectations and acknowledging that the implementation process may have some challenges can prepare employees for any temporary disruptions.
Examples of ERP Systems

Odoo ERP
Odoo is a widely acclaimed open-source ERP solution known for its flexibility and user-friendliness. Its modular approach allows businesses to customise and integrate specific modules based on their unique requirements. Odoo's community edition is available as open-source software, while the enterprise edition offers additional features and support.
Key Features and Modules
Accounting
Odoo's accounting module enables efficient financial management, including invoicing, billing, bank reconciliation, and financial reporting.
Human Resources
The HR module streamlines employee management, payroll processing, leave management, and performance evaluation.
Sales and CRM
Odoo's CRM module facilitates lead management, sales automation, customer communication, and marketing campaigns.
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Enables to manage inventory, track stock movements, and optimise warehouse operations.
Manufacturing
This module assists in production planning, scheduling, quality control, and work order management.
Project Management
This module supports project planning, task allocation, progress tracking, and resource management.
SAP ERP
SAP ERP is a widely used solution favored by large enterprises and multinational corporations. It offers a range of industry-specific functionalities and integrates various business processes seamlessly.
Key Features and Modules
Financial Management
SAP ERP's financial module provides comprehensive accounting and financial reporting capabilities.
Human Capital Management (HCM)
HCM encompasses employee administration, payroll, talent management, and workforce analytics.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SAP ERP's SCM module enables efficient procurement, inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics.
Production Planning
The production planning module supports optimised production scheduling, shop floor control, and quality assurance.
Sales and Distribution
This module streamlines sales processes, order processing, and customer service.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
This module facilitates customer engagement, marketing, sales automation, and customer service.
SAP ERP is known for its robustness and integration capabilities, allowing businesses to achieve a high level of operational efficiency and data visibility across various departments. However, it is essential to note that SAP ERP implementation can be complex and may require significant investment in terms of licensing and customisation.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based ERP and CRM solution that seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products. Its user-friendly interface and adaptability make it suitable for businesses of all sizes, from small enterprises to large corporations.
Key Features and Modules
Finance and Operations
This module handles financial management, supply chain, manufacturing, and project accounting.
Sales and Marketing
Encompass sales automation, lead management, customer service, and marketing automation.
Human Resources
Streamlines talent acquisition, onboarding, employee records, and performance management.
Retail
Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Retail offers point-of-sale (POS) solutions, inventory management, and omnichannel retail capabilities.
Project Service Automation
This module enables project planning, resource scheduling, and project tracking.
Field Service
Field service capabilities include work order management, resource scheduling, and mobile field access.
Oracle ERP Cloud
Oracle ERP Cloud is a comprehensive cloud-based ERP solution offered by Oracle Corporation. It caters to businesses of all sizes, providing a suite of integrated applications to streamline various business processes.
Key Features and Modules
Financials
Oracle ERP Cloud offers a comprehensive financial management system, including general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and cash management.
Procurement
This module handles procurement processes, including sourcing, purchasing, and supplier management.
Project Management
Encompasses project planning, budgeting, resource management, and project costing.
Supply Chain Management
This module optimises supply chain processes, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics.
Human Capital Management (HCM)
Oracle's HCM module manages employee data, payroll, benefits, and performance management.
Conclusion
ERP systems have transformed businesses by streamlining processes, enabling better decision-making, and promoting collaboration among departments. The examples of Odoo, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and Oracle ERP Cloud demonstrate the diverse capabilities and benefits of ERP solutions for organisations of different sizes.
Among the ERP systems, Odoo ERP software solutions stand out for several reasons. Its open-source nature provides a cost-effective solution, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. The ability to customise and integrate modules allows for a tailored and agile ERP experience that aligns with specific business needs.
Odoo's modules cover various business functionalities, offering a comprehensive suite of applications for finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and CRM. The user-friendly interface and intuitive design promote easy adoption and smooth navigation for employees.
Furthermore, Odoo's cloud-based deployment option ensures scalability, data security, and remote access to critical business information. Regular updates and community support keep Odoo up-to-date with the latest features and improvements.
Lastly, Odoo ERP emerges as a robust and versatile solution that empowers businesses with an integrated and efficient approach to managing their operations effectively.